
.NET supports the Dependency Injection (DI) software design pattern, which Microsoft describes as a technique for achieving Inversion of Control (IoC) between classes and their dependencies, such that components receive their dependencies from an external source (usually a framework or container), allowing the caller to provide necessary dependencies rather than the component creating them internally.
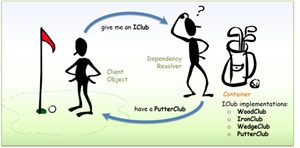 [Click on image for larger view.] The DI Design Pattern in a Golf Analogy (source: Microsoft).
[Click on image for larger view.] The DI Design Pattern in a Golf Analogy (source: Microsoft).
For those new to DI and IoC, the concepts can be challenging to grasp. To help developers understand the "what" and "why" of the technique, Jeremy Clark, a developer, consultant and educator who provides "byte-sized chunks of .NET" on his Jeremy Bytes site, will present a session titled "DI Why? Getting a Grip on Dependency Injection" at the upcoming Visual Studio Live! developer conference taking place August 5-9 at Microsoft Headquarters in Redmond, Wash.
"We'll look at the problems caused by tight coupling," said the Microsoft MVP for .NET. "Then we'll use some DI patterns such as constructor injection and property injection to break that tight coupling. We'll see how loosely coupled applications are easier to extend and test. With a better understanding of the basic patterns, we'll remove the magic behind DI containers so that we can use the tools appropriately in our code."
Attendees of the 75-minute introductory/intermediate-level session are promised to learn to:
- See the problems that DI can solve
- Understand DI by using it without a container
- See how a DI container can add some magic and reduce some code
We caught up with Clark to get a preview of his session and to learn more about the benefits of DI in modern software development in a Q&A.
VisualStudioLive! What inspired you to present a session on this topic?
Clark: When I was first introduced to DI, I was given an existing application that used a DI container and basically told, "Good luck." I had to do quite a bit of reading and exploration to understand why the application needed DI and also exactly what the DI container did.
 "This session is the resource I wish I had when I was learning: the 'what' and 'why' of Dependency Injection."
"This session is the resource I wish I had when I was learning: the 'what' and 'why' of Dependency Injection."
Jeremy Clark, Developer Educator
This session is the resource I wish I had when I was learning: the "what" and "why" of Dependency Injection.
DI has been around for a long time. Is it still relevant?
DI is even more important today than when I started using it. ASP.NET Core has a built-in DI container (whether you explicitly use it or not). And when we use the new project templates to create an application with controllers (either MVC or API controllers), an "ILogger" is injected as part of the controller constructor.
public class HomeController : Controller
{
private readonly ILogger<HomeController> _logger;
public HomeController(ILogger<HomeController> logger)
{
_logger = logger;
}
// additional code omitted.
}
If you are not familiar with DI, your reaction might be, "What is this ILogger, and where does it come from?" But with a good handle on DI, the code is much more approachable: "This is an injected logger dependency, and the DI container makes sure that we have a valid logger available to us here."
And if you use ASP.NET Core Minimal APIs, the DI container is just as useful to make sure you have everything you need for each of your endpoints.
Can you elaborate on the specific problems that DI aims to solve in modern software development?
Our code has dependencies. Some examples: a data supplier, a user authorization validator, an error logger. When we "new" up these dependency objects inside a class, we are not only getting the functionality but also choosing how that functionality is implemented. This is referred to as tight coupling.
Let's take an example: we need logging throughout our application. Each class news up a ConsoleLogger object to write logs to the console. In this scenario, each class is not only getting functionality (logging), but also choosing how that logging is implemented (logging to the console). This creates a tight-coupling between our class and it's dependency on a particular logger. Now imagine that we need to change to a different logging implementation: we would need to change all of the classes that use a logger.
With DI, instead of newing up a logger in the class, we specify that we need logging functionality (such as asking for an ILogger implementation with a constructor parameter). A fully functional logger is then injected into the class -- often by a DI container. Now our class only cares about the functionality (logging) and does not care about the specific implementation. If we need to change to a different type of logging, we only need to update things in one place (our DI container). We do not need to touch our existing classes at all. This is referred to as loose coupling; and it offers a number of advantages.
How does DI facilitate the creation of loosely coupled applications, and why is this important?
Loosely coupled applications let us take a more modular approach to our code. This lets us create functionality and change things quickly. With loosely coupled pieces, we can snap in a relevant piece of functionality (such as a sales tax calculator based on a specific location). We can swap out one piece of functionality for another (such as changing from a local file-based data store to a cloud-based distributed one). We can replace a piece of functionality with a fake or mock for unit testing. We can also un-snap pieces, add functionality in-between (called "interception"), and snap things back together again with minimal (or no) changes to our existing objects. I often use this last scenario to add data caching or retry functionality.
Also, with modularity in mind, our loosely coupled pieces isolate functionality. We have certain pieces for business logic, certain pieces for logging, certain pieces for data access, and certain pieces that handle user interaction. When something goes wrong, it's easier to find the problem due to this isolation -- the functionality is in a specific part of the code. (And good unit tests also help us quickly pinpoint where things go wrong.)
What are one or two common pitfalls developers encounter when implementing Dependency Injection for the first time, and how can they be avoided?
One common pitfall is not really "getting" DI. If we need to change or add to an application that already has DI, we copy and paste some code, make a few adjustments, and then cross our fingers and hope that it works. This session is all about making sure that we understand those core concepts. Then we can use DI intentionally and understand the changes that we make.
Another common issue is over injection -- getting too excited about DI and injecting as much as we can in our applications. The result is complexity without benefit, and overly complex applications are no fun to support. One way to fix this is to be aware of what types of dependencies we need to inject. Start by focusing on the things that are likely to change, on places where we may need to add functionality, and on classes or systems we may want to fake for testing purposes. I generally advise newcomers to inject dependencies only when they have a good reason for it. As experience grows, you will get better at determining which items are good candidates for DI.
Could you discuss the differences and use cases for constructor injection versus property injection?
One of the great things about Dependency Injection is that there is more than one way to do it. A few primary patterns are constructor injection, property injection, and method injection.
Constructor injection forces us to provide a dependency. With constructor injection the dependency is injected as a constructor parameter. When someone creates the object, they must also supply the dependency as an argument. I usually default to constructor injection because it makes the dependency obvious (it's right there in the constructor parameters), and the dependency can be made available to the entire class. For example, I may need an object that supplies data. This dependency is not optional, and I want someone to specifically supply that object to the class. Constructor injection is a good pattern here.
Property injection is good for optional dependencies. With property injection, the dependency is injected as a property on the class. Commonly the property will have a default value (which may have no functionality). When someone creates the object, they do not need to supply the dependency. If they want to override the default, they can assign a value to the property; otherwise, the default will be used. This is great if the dependency is truly optional. As an example, logging may be an optional dependency. My class can have a default logger property that does nothing. But if someone needs logging, they can override the property with a logger of their choosing (such as logging to the console or logging to a database).
One downside to property injection is that the dependency is a bit hidden. We may not know that the property exists or that we can override it. This is why I generally choose constructor injection unless something is truly optional.
The session mentions using DI without a container. Could you describe a practical example of this and explain the benefits?
DI containers are awesome. They handle a lot of work for us, but they also hide what they do. When someone is new to DI, there may be confusion between DI (meaning the concepts and patterns of DI) and the implementation (the details of the DI container). By using the DI patterns without a container, we take a more hands-on approach to see how DI works and why we get the benefits that we do. We also see that we may not need a DI container for straight-forward scenarios with small numbers of objects. Once things get a bit more complex, it's great to have a DI container handle most of the work for us. And if we have a solid foundation in DI concepts, then we can be more confident that we are using a DI container effectively.
How does a DI container "add some magic" to the process, and what are the implications for code reduction?
When we use a DI container, our code is more declarative. For example, we can configure the container with a mapping between an interface (such as ILogger) and the actual type we want to use (such as a ConsoleLogger). When we ask the container for an object that needs a logger, the container handles the details of creating things and makes sure that our object gets the right logger. This is all code that we do not have to write.
A DI container handles many more details for us as well. It figures out how to create objects for us, including automatically injecting any dependencies that are needed for that creation. In addition, the DI container deals with the lifetime of the objects -- whether to keep an object around to re-use it later or to create a new instance each time we need it. As developers, we configure the lifetime based on factors such as how much memory is used or how frequently a particular object is needed. But we can leave all of the details on exactly how that happens up to the DI container.
For those new to DI, what resources or practices do you recommend to deepen their understanding and skill set?
I learn well with books, so I tend to recommend "Dependency Injection: Principles, Patterns, and Practices" by Steven van Deusen and Mark Seemann. This is a bit of an older book (from 2019), but one of the great things about patterns and concepts is that they don't change. So even if we are using different DI containers today than we were 5 years ago, we are still using the same concepts to understand them.
I also have several articles that dive deeper into topics such as different ways to implement Property Injection, using the Decorator pattern to add logging, caching, and re-try functionality, and how to use DI to help test "DateTime.Now." Links to these articles can be found here.
Looking beyond the basics, what advanced DI techniques or patterns should developers aim to learn?
There are quite a few topics to explore in Dependency Injection. Here are a few I recommend when you're ready to learn more:
- Lifetime Management: Common lifetimes are Singleton, Scoped, and Transient. This determines whether an object is created new each time or whether it is re-used (and the scope of where it is re-used). Which you choose depends on the needs of your application.
- Stable vs. Volatile Dependencies: Which dependencies are likely to change? Which dependencies do we have control over? These are questions that help us determine whether a dependency is stable or volatile -- and in turn, whether a dependency is a good candidate for Dependency Injection.
- Auxiliary Patterns: The Decorator Pattern, Proxy Pattern, and Null Object Pattern are not directly related to Dependency Injection, but they can be very useful. For example, in the session, we use the Decorator Pattern to add caching functionality in the demo. We can use these auxiliary patterns to make our DI more effective.
- Using Factory Methods with DI Containers: DI containers are really good at using constructors to create objects. But sometimes we need to use a factory method instead. Fortunately for us, DI containers have a way to specify a factory method to use for an object. Be sure to check on how to do this for your preferred container.
Note: Those wishing to attend the conference can save hundreds of dollars by registering early, according to the event's pricing page. "Register for VSLive! at Microsoft HQ by the Early Bird deadline of June 7 to save up to $400 and secure your seat for intensive developer training at Microsoft HQ in Redmond!" said the organizer of the developer conference.
Posted by David Ramel on 05/21/20240 comments

Back in January, I predicted this would be the year of AI. In February I gave you an introduction to GitHub Copilot. Now, with the general availability release of GitHub Copilot in the CLI, you can have all the power of AI and GitHub Copilot while never having to leave the safety of your command line.
AI integration in development tools has transformed the landscape of coding and software design. AI can analyze vast amounts of code to provide context-relevant suggestions, anticipate errors and offer solutions, effectively acting as a pair programmer with access to the world's programming knowledge. This leads to faster debugging, more efficient code writing and, ultimately, higher-quality software projects.
For many developers, the command line is a control center. It offers speed, precision and a streamlined interface that GUIs often can't match. By integrating AI tools directly into the command line, developers can maintain their workflow's rhythm without switching contexts, which is crucial for maintaining focus and productivity.
GitHub Copilot in the CLI
GitHub Copilot, available as an extension in multiple IDEs, now extends its capabilities to the command line interface. GitHub Copilot in the CLI provides a chat-like interface in your terminal that allows you to ask questions about the command line. You can ask GitHub Copilot to provide either command line suggestions or to explain given commands.
For example, you can use Copilot to help you craft the right command for a given task, which could be a shell command, git command or even how to use the GitHub CLI itself. You can also give Copilot a command you don't understand, and it will explain it to you using natural language. To really understand what is going on, let's see this in action.
Using GitHub Copilot in the CLI
To get started using GitHub Copilot in the CLI, you first need to install the GitHub CLI. The GitHub CLI is an open source tool for using GitHub from your computer's command line. Using it, you can do most things you can do in the GitHub GUI without leaving your command prompt. And one of those things is to use GitHub Copilot.
Next, we need to install the GitHub Copilot in the CLI extension into the GitHub CLI. This is done by running the GitHub CLI extension install command:
gh extension install github/gh-copilot
Note: You will need a GitHub Copilot Individual, Business or Enterprise license to use GitHub Copilot in the CLI.
After installing the extension, and running "gh auth" to login, you are ready to start using Copilot in the CLI.
Explain a Command
You can ask Copilot in the CLI to explain a shell, git or GitHub CLI command using the "explain" command. For example, the following git command is used by many developers to view their git history:
git log --oneline --graph --decorate --all
You can run:
gh copilot explain "git log --oneline --graph --decorate –all"
and it will explain what the command is doing, as shown in Figure 1.
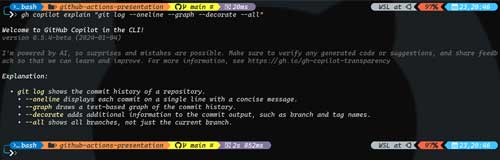 [Click on image for larger view.]
[Click on image for larger view.]
Figure 1. Copilot in the CLI explaining the git log command.
Here is another example of Copilot explaining what the "sudo apt-get" command does.
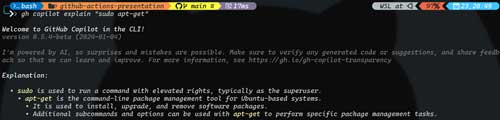 [Click on image for larger view.]
[Click on image for larger view.]
Figure 2. Explaining the sudo apt-get command.
Copilot in the CLI explains commands in plain language, making it easy for you to understand what the command is doing. You don't have to worry about going through documentation because Copilot's explanation includes information about command input and output and can even provide practical examples for you to use.
Suggest a Command
You can ask Copilot in the CLI to suggest a shell, git or GitHub CLI command using the "suggest" command. For example, let's say you want to find all the JavaScript files that are older than 10 minutes, excluding the node_modules folder. You could probably search Stack Overflow and maybe find an answer that gets you part of the way there. Or, you could use Copilot, and run the following command:
gh copilot suggest -t shell "find all javascript files older than 10 minutes, excluding the node_modules folder"
Figure 3 shows the results of running this command. As you can see, after you ask Copilot for help, you then have the option of continuing to revise the answer, copying it to the clipboard to use it, or even having it explained to you.
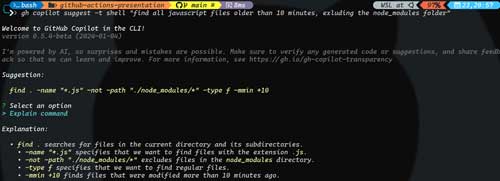 [Click on image for larger view.]
[Click on image for larger view.]
Figure 3. Asking for help on how to find JavaScript files older than 10 minutes.
Conclusion
Integrating AI tools like GitHub Copilot in the CLI into the command line not only streamlines the development process but also significantly boosts productivity and code quality. By leveraging these tools, developers can enjoy a seamless, intuitive AI-enhanced coding experience that aligns with the dynamic demands of modern software development.
As the field of AI continues to evolve, we can anticipate even more sophisticated tools that further integrate AI into the developer's toolkit, making the command line an even more powerful ally in the quest for efficient and innovative software development.
Posted by Mickey Gousset on 04/25/20240 comments

It only takes 20 minutes to upgrade your Git game in Visual Studio 2022, and Jessie Houghton, Visual Studio Program Manager at Microsoft, will show you how at the August 5-9 Visual Studio Live! developer conference being held at Microsoft headquarters in Redmond, Wash.
In their "Fast Focus" session, you'll learn how to leverage the newest Git features to your daily advantage (think AI assistance) and gain confidence in navigating common pitfalls, all with Git and GitHub.
Specifically, attendees are promised to learn how to:
- Leverage the newest Git tooling and GitHub updates
- Level up your Git usage to superpower you or your team's productivity
- Navigate common Git pitfalls
We caught up with Houghton to learn more about their session in a short Q&A.
VisualStudioLive! What inspired you to present a session on this topic?
Houghton: As the product manager for the Visual Studio Git tooling team, I spend my time talking to customers and creating new features to help solve their issues with version control. Presenting on these new features help more people learn about them and benefit from what's built into their favorite IDE!
 "Lots of people are comfortable with the very basics of Git, but the Visual Studio Git tooling UI can empower you to master powerful, advanced topics that are difficult to learn from the CLI alone."
"Lots of people are comfortable with the very basics of Git, but the Visual Studio Git tooling UI can empower you to master powerful, advanced topics that are difficult to learn from the CLI alone."
Jessie Houghton, VS Program Manager, Microsoft
Lots of people are comfortable with the very basics of Git, but the Visual Studio Git tooling UI can empower you to master powerful, advanced topics that are difficult to learn from the CLI alone.
Can you describe just one recent Git tooling feature introduced in Visual Studio 2022 and its significance for developers?
A favorite of mine is the multi-branch graph. Using Visual Studio to visualize your feature branch in relation to the main development branch gives you confidence when rebasing or merging changes. It demystifies the underlying concepts that govern how Git works, and it unlocks easier cherry-picking and comparing across branches. Learn more from the feature release blog, Multi-Branch Graph Available for General Audiences.
How does the integration of AI assistance with Git tooling enhance productivity and version control management in Visual Studio 2022?
One of the primary benefits of version control is access to the entire history of the project. Good documentation in commit messages and pull request descriptions empower teams to move faster and create better products. For example, when looking to diagnose a bug or implement a similar feature to an existing one, a descriptive commit message can make it super obvious which parts of the code are important to dig into and what important decisions went into an implementation. On the other hand poor quality messages require you to spend more time trying to figure out manually why the code works a certain way. The major problem we stumble into is that writing good documentation is tedious! AI is a great fit to solve this problem! By generating the first draft of your commit message or pull request description, AI empowers you to spend less time writing documentation and more time writing code, while reaping all of the benefits of history listed above. Also, even if you come across a poor description in the history, AI can explain those commits as well, helping you parse through large commits with ease.
What are one or two common Git pitfalls that developers face, and how does this session aim to address them?
Demonstrating the new AI features will help address the common pitfall of dealing with poor quality Git history, as was mentioned above. Another nightmare for developers is recovering from Git mistakes. We all make them, but fixing them in the command line is a painful process of looking up commands we rarely use. I'll share some common mistakes and their corresponding easy recovery mechanisms that the Visual Studio Git tooling offers you.
With the continuous updates to GitHub and Git tooling, how should developers stay informed and proficient in these changes?
Check out my posts on Visual Studio DevBlogs and all of the other great Visual Studio updates hosted there, as well.
In terms of collaboration and project management, how do the new features in Git and GitHub improve the workflow for teams?
One example was detailed above. For most teams, version control is a requirement, so learning how to maximize the efficiency of your interactions with Git allows you to focus more on your code. For example, using features like referencing GitHub issues in your commits helps your teammates stay updated on your work and can update the backlog automatically.
For someone looking to "level up" their Git usage, what foundational practices would you recommend mastering first?
We've got an entire learning library on YouTube with Beginner, Intermediate, and Advanced content to help you at any level of Git usage, Git Tooling in Visual Studio - YouTube. The beginner series will get you started with the most important basics and major work flow.
How do the enhancements in Visual Studio 2022's Git tooling reflect the evolving needs of modern software development?
Version control is an integral tool for the modern software developer. There are no more excuses for code to not be managed, backed up, and hosted in the cloud on GitHub. Coupled with the exciting demands of an AI transformed world, developers need their IDEs to keep up with the demand to provide solid version control integration and AI driven innovation.
What advice do you have for developers who are looking to seamlessly integrate these new Git features into their existing projects?
If you haven't checked out the Git tooling in Visual Studio in a while, take a second look. We've made tons of improvements and added additional features that may make you second guess using the command line. If you're not using Git already, click the "Add to Source Control" button in the status bar in Visual Studio to get started.
Note: Those wishing to attend the conference can save hundreds of dollars by registering early, according to the event's pricing page. "Register for VSLive! at Microsoft HQ by the Early Bird deadline of June 7 to save up to $400 and secure your seat for intensive developer training at Microsoft HQ in Redmond!" said the organizer of the developer conference.
Posted by David Ramel on 04/18/20240 comments
As software projects get more complex, managing dependencies becomes an increasingly critical task for developers. Dependencies, the external packages or libraries that your project relies on, can significantly impact your application's security, maintainability and compatibility. This is particularly true in the .NET ecosystem, where projects often rely on a vast array of NuGet packages.
In this article, we'll explore effective strategies for managing these dependencies, with a focus on identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities, leveraging tools such as GitHub Dependabot, and discussing other open source alternatives that can bolster your security posture.
Understanding Dependency Management
Before diving into the tools and practices, it's essential to grasp what dependency management entails. Dependency management involves:
- Identifying dependencies: Knowing what libraries or frameworks your project relies on.
- Vulnerability tracking: Monitoring dependencies for any security vulnerabilities and addressing them promptly.
The Importance of Keeping Dependencies Updated
Regularly updating dependencies is crucial for several reasons. Primarily, it ensures your application is secure from known vulnerabilities often patched in later versions of the dependencies. Moreover, updates can bring performance improvements, new features and compatibility with newer technologies, enhancing your project's overall quality and lifespan.
One of the biggest areas where I see developers mess up is not checking to see if the dependencies in their code have security vulnerabilities open against them. This is especially true with code that hasn't been updated in several years, but is still being used in production. Security vulnerabilities in code like this could lead to intellectual property losses, data breaches and worse.
Tools for Managing Dependencies
If you use GitHub, then GitHub Dependabot is an invaluable tool that automates the monitoring and updating of dependencies -- and it's free.
Integrated directly into GitHub, Dependabot scans your project's dependency files (such as `.csproj` or `packages.config` for .NET projects) and compares the package versions you are using against the GitHub Advisory Database. If it finds you are using a vulnerable package, it will open an alert in the repository, as shown in Figure 1. This alert gives you details of the vulnerability, as well as information on what version of the package to upgrade to in order to resolve the vulnerability.
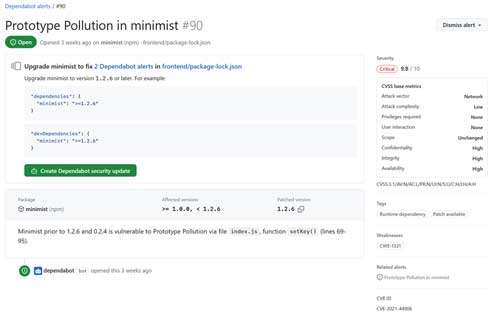 [Click on image for larger view.] Figure 1. Dependabot Alert
[Click on image for larger view.] Figure 1. Dependabot Alert
Dependabot can also automatically generate pull requests to update the code to the non-vulnerable new version, and can even let you know when new versions of the package become available.
As mentioned, Dependabot is free for GitHub users. There is also a paid version available for Azure DevOps users as part of GitHub Advanced Security for Azure DevOps.
Other Open Source Tools
While Dependabot is a powerful tool for managing dependencies, several other open source tools can complement its capabilities:
- NuGet Package Explorer: A Windows application that allows you to view the contents of NuGet packages, explore their dependencies and determine the package's compatibility with different versions of .NET. This tool is essential for manually reviewing dependencies before incorporating them into your project.
- OWASP Dependency-Check: An open source tool that identifies project dependencies and checks if there are any known, publicly disclosed vulnerabilities. Although it requires manual setup and integration into your build process, its comprehensive database of vulnerabilities makes it a valuable tool for .NET developers.
- Snyk: Though not entirely open source, Snyk offers a free tier and integrates well with .NET projects. It scans dependencies for vulnerabilities and provides detailed remediation guidance. Snyk can run within your CI/CD pipeline, ensuring vulnerabilities are caught early in the development cycle.
Best Practices for Dependency Management
To effectively manage your .NET project dependencies, consider the following best practices:
- Regularly Review and Update Dependencies: Leverage tools like Dependabot to automate this process, but also allocate time for manual review, especially for major version updates that might introduce breaking changes.
- Adopt a Security-First Mindset: Prioritize security updates and apply them as soon as possible. Use tools like OWASP Dependency-Check and Snyk to identify potential vulnerabilities and address them promptly.
- Understand Your Dependencies: Before adding a new dependency, evaluate its necessity, license compatibility and its own dependency tree. This can prevent introducing unnecessary risks into your project.
- Educate Your Team: Ensure that all team members understand the importance of dependency management and are familiar with the tools and practices you've adopted. This collective awareness can help maintain a secure and stable codebase.
Effective dependency management is a cornerstone of modern software development, particularly in complex ecosystems like .NET. By leveraging tools such as GitHub Dependabot and incorporating other open source solutions into your workflow, you can significantly enhance the security and maintainability of your projects.
Remember, the goal is not just to react to vulnerabilities but to proactively manage your dependencies to prevent issues from arising. With the right tools and practices, you can.
Posted by Mickey Gousset on 03/26/20240 comments

Remember when TypeScript, or C#, or even C++ was new, and you wished you'd known they were going to "be big" so you could be the person ahead of the curve instead of struggling to catch up to where everybody else seemed to be already?
To help stay ahead of that curve, longtime software development expert Ted Neward takes the time to continually scour the coding landscape -- he actually pores through GitHub repos, for example -- to look for new languages that might not be what you end up using in your day job in 2025, but which could expose and refine the concepts that define the language that will.
One thing that he's looking for is a language that ups the abstraction game, providing a means, for one example, to automatically handle memory management, an onerous, time-consuming (and often blatantly unsafe) task that had to be done manually in C++ but is taken care of natively by languages such as Rust.
Neward shares his expertise in major developer conferences, and his next stop is at Visual Studio Live! Chicago, where he'll present "Busy Developer's Guide to Next-Generation Languages."
Attendees are promised to:
- Learn different approaches to coding
- Take away a different way of thinking about building apps
- Get a glimpse into the potential future
We caught up with Neward to get a sneak peek into his session and to learn more about the next-generation languages he's been tracking.
VisualStudioLive! What inspired you to present a session on next-generation languages?
Neward: For the last decade I've been awaiting the next round of languages that elevate our abstraction level another notch, and I've been somewhat disappointed that they haven't seemed to take root. There's a lot of interesting ideas out there, and I'm pretty sure that if developers (and their management) can get a sense of what we gain by taking this next step up, we'll gain as an industry -- in productivity, in reduction in cognitive complexity, and in security and quality, among other things.
Can you briefly explain what a next-generation language is?
Basically, a language that takes a significant step away from the dominant paradigm (object-oriented or object/functional hybrid) and introduces something "new" into the mix.
 A next-generation language "takes a significant step away from the dominant paradigm (object-oriented or object/functional hybrid) and introduces something 'new' into the mix."
A next-generation language "takes a significant step away from the dominant paradigm (object-oriented or object/functional hybrid) and introduces something 'new' into the mix."
Ted Neward, Principal, Neward and Associates
Could you provide one example of a next-generation programming language that you believe is poised to make a significant impact in the future?
Sure: One language to have a look at is Ballerina, a service-oriented programming language that runs on top of the JVM. Because it puts services (that is to say, the same things we talk about when we speak of HTTP APIs, but it goes beyond HTTP in a big, and quite natural, way) front-and-center in the language, we find that writing a new service from scratch turns into one, maybe two files, and a dozen lines of code at most, to get a Docker image fully ready-to-deploy in any cloud service you care to name. Most OO languages have a really hard time keeping up with that, because they're built to solve a different problem.
What are a couple of examples of the different approaches to coding that these next-generation languages encourage? How do they differ from traditional programming paradigms?
The first, already mentioned, is that of service-oriented: What happens when we make services a first-class construct? Or let's think about UI: so much of what we do is write a bunch of objects that have to work together -- what if we took a look at abstracting one level up, and treated the web (HTML/CSS/JS) as an implementation detail rather than something the developers have to stare in the face all the time? What if we elevated user interface to a set of language constructs?
How might these emerging languages influence the way we think about and approach app development? Can you give an example of how they could change our current development practices?
Typically, when we elevate a level of abstraction, we gain a significant reduction in visible complexity -- developers don't have to worry so much about physical details, so we're able to spend less lines of code on dealing with physical restrictions. Other object-oriented or object-functional language/framework combinations try to accomplish this (React, Angular and so on), but we still get tripped up on all these niggling details.
Consider this: when we wrote code in C++, we had to spend half the code dealing with memory management. When we elevated the abstraction level to memory-managed languages like Java and C#, suddenly a whole lot of worries about physical details (memory management) went away, and we were able to free up brain space for other things.
Drawing from your experience, how do you predict which programming languages or concepts will become more prominent in the future? What indicators do you look for?
Oh, if I were any good at that, I'd have made a lot more money as a fortune teller! A large part of the process is to examine the problems we currently deal with as developers.
For developers who want to stay ahead of the curve, what strategies would you recommend for learning and adapting to these next-generation languages? How can they prepare themselves for the shifts in programming trends?
Frankly, one way I stay ahead of the curve is to do some aggressive browsing -- for example, I'll go up to GitHub, and do a repository search for "programming language" just to see what comes up. Most of the first five pages are recognizable, like Python or Ruby, but once you get past the mainstream open-source languages, you find some really interesting candidates.
How can developers evaluate the long-term viability and industry adoption potential of a new programming language? What factors should they consider when deciding whether to invest time in learning one of these languages?
Does it solve an actual problem? Does it let you not worry about something, or let you build a thing in fewer lines of code than with your traditional language of choice? Does it allow you to do some things at a design level that would be really tricky or expensive to do now?
Take a reasonably small problem (something larger than a TODO list, for example) and try building it using the new language, and see how well or how fast it goes. Don't expect that you'll convince anybody at work to use it right away, but you never know -- if it solves a problem the company is staring down, and the company is committed to using technology as a competitive advantage, you could very well be the person that brought the company the advantage they needed over their competitors!
Note: Those wishing to attend the conference can save hundreds of dollars by registering early, according to the event's pricing page. "Register for VSLive! Chicago by the March 1 Super Early Bird deadline to save up to $400 and secure your seat for intensive developer training in Chicago!" said the organizer of the developer conference.
Posted by David Ramel on 02/27/20240 comments

This quick reference guide shares 15 must-know shortcuts for improving efficiency and productivity in Visual Studio. Master shortcuts for debugging, refactoring, formatting, searching, and more!
Get the PDF!
Sign up below to access the guide “15 (More) Great Visual Studio Keyboard Shortcuts”. Fill out the sign-up form with your name and email address, then use the password provided to access the PDF. Save or print out these useful shortcuts to keep handy while coding for improved speed and efficiency in Visual Studio.
Posted on 02/26/20240 comments

As a small teaser for my upcoming Copilot Engineering Everywhere workshop at VSLive! Las Vegas, I thought I'd give you an introduction to GitHub Copilot.
In the rapidly evolving landscape of software development, AI has emerged as a game-changer, offering tools that augment human capabilities and making coding more efficient and accessible. In this article, we'll explore what GitHub Copilot is, explain how it works and walk you through a simple demo to get you started.
What Is GitHub Copilot?
GitHub Copilot is a cutting-edge AI-powered code completion tool developed by GitHub and powered by a generative AI model developed by GitHub, OpenAI and Microsoft. It acts as an intelligent assistant for developers, suggesting entire lines of code or even whole functions as you type. GitHub Copilot is designed to understand the context of your code, making it possible to suggest relevant code snippets, implement patterns, and even generate code for new projects based on the description in comments.
As you type in your code editor, GitHub Copilot dynamically analyzes the context of your codebase and the comments you write to suggest relevant code snippets. These suggestions can be accepted, modified or rejected, providing a seamless coding experience that can significantly speed up the development process.
Getting Started with GitHub Copilot
To demonstrate the power of GitHub Copilot, let's go through a simple Python project where we'll create a function to calculate the factorial of a number. You will need the following if you want to try this yourself:
- Visual Studio Code (VS Code) installed
- GitHub Copilot extension installed in VS Code
- An active GitHub Copilot subscription
Let's run through the following steps:
1. Open VS Code and create a new Python file named "factorial.py."
2. Let's add a comment at the top of the file describing, in a couple of sentences, what we are trying to accomplish. This helps set the context for GitHub Copilot. We are going to add the following comment block to the top of my file:
# I want to write a function that takes a number and returns the factorial
# of that number. I will use a recursive function to do this. I also want to
# write the appropriate code to call the function and print the result.
3. As we press Enter, GitHub Copilot suggests a complete function implementation for calculating the factorial. You can accept the suggestion by pressing Tab or Enter, and the entire code block will be inserted into our file.
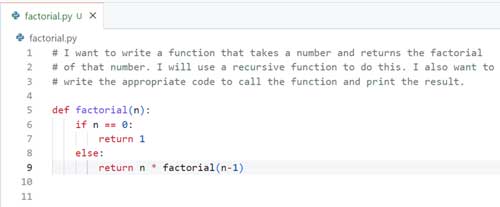 [Click on image for larger view.] Figure 1.
[Click on image for larger view.] Figure 1.
4. Press Enter a couple more times, and it suggests the code to call the function to test it, along with the expected results.
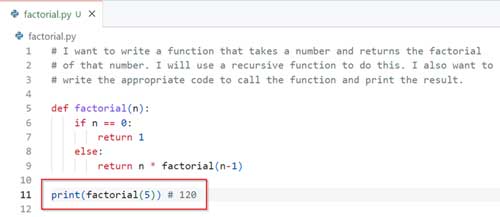 [Click on image for larger view.]
Figure 2.
[Click on image for larger view.]
Figure 2.
5. Run the code and confirm that it returns the correct results.
This is just a basic introduction to using GitHub Copilot. As you can see, it generated all the code for us based on our initial comments at the top of the file. We can add more comments directly in the file to ask GitHub Copilot to assist us with whatever we might need -- for example, creating other functions or code relevant to our project.
What I have shown above just scratches the surface of the GitHub Copilot ecosystem. There is also GitHub Copilot Chat, which is a chat interface directly in your IDE where you can ask Copilot coding-related questions.
GitHub Copilot in Modern Development
GitHub Copilot represents a significant leap forward in how developers write code. It not only speeds up the coding process but also helps in learning new languages and frameworks by providing contextually relevant suggestions. We are not Python developers and don't know the Python language. But using Copilot, as shown above, we were able to create a Python script to accomplish our task.
GitHub Copilot is more than just a code completion tool; it's a glimpse into the future of software development, where AI partners with humans to enhance creativity and efficiency of coding. Whether you're a seasoned developer or just starting, GitHub Copilot offers a unique opportunity to enhance your coding experience and take your projects to the next level.
And I'll leave you this teaser: If you do decide to attend my workshop, you'll learn more about both GitHub Copilot, as well as how to use Microsoft and open-source tools to build your own Copilot. Happy coding!
Posted by Mickey Gousset on 02/23/20240 comments

You wouldn't really name a variable "x," would you?
But it happens.
And it's not just "x." It's "usrdb," "item," "foo," "test," "blah" and more. These are real variable names that have been encountered in production-grade codebases.
"And that's just scary!" says Adrienne Braganza-Tacke.
The senior developer advocate at Cisco has become a specialist in naming variables, which is actually more complicated and important than it may seem at first. Luckily, she's bringing her expertise to the Visual Studio Live! developer conference in Chicago, where she'll present a session titled "Variables of the Veracious Variety: How to Better Name your Variables" on April 30, 2024.
The very existence of such a presentation brings to mind the famous quote by Phil Karlton: "There are only two hard things in computer science: cache invalidation and naming things."
Attendees of the introductory/intermediate 75-minute session won't be learning anything about cache invalidation, but they will be learning about the importance of naming things and how to do it better, being promised to:
- Understand what makes variable naming difficult
- Recognize what makes a variable clear, concise, and consistent
- Explore variable naming patterns for almost any type of variable
We caught up with Braganza-Tacke to get a preview of her session, and to learn more about the importance of naming variables in software development.
VisualStudioLive!: What inspired you to present a session on naming variables?
Braganza-Tacke: I tend to talk about topics that I think every software developer should be knowledgeable about and variable naming is one of them. What really inspired me to put together a whole talk, though, was just how many bad variable names there are in real-world applications. x, usrdb, item, foo, test, blah ... these are real variable names I've encountered in production-grade codebases. And that's just scary! As with most of my talks, there's a lot of common software development sense that's not so common. That's why I'm putting my decade of experience, team-tested trials, and actionable advice together into one nice talk for anyone that wants to level up their variable naming!
What are some common challenges developers face when naming variables, and why is it often considered one of the harder tasks in computer science?
Typically, it's really hard to get the essence of a concept down to a single word or very short phrase; how do you convey a customer that has surpassed the maximum number of refund transactions allowed in a month as clearly and concisely as possible? Now, take that thought experiment and consider that different words mean different things to different people. The same words can even have different meanings or connotations within different contexts. Add onto that the global nature of software development, where English is not always the first language of the developer.
 "Developers are basically asked to choose variable names that convey a concept that is also explicitly clear to their team, can't be confused with other concepts, and makes sense within the context of the codebase they are working in."
"Developers are basically asked to choose variable names that convey a concept that is also explicitly clear to their team, can't be confused with other concepts, and makes sense within the context of the codebase they are working in."
Adrienne Braganza-Tacke, Senior Developer Advocate, Cisco
Taking all of this into consideration, developers are basically asked to choose variable names that convey a concept that is also explicitly clear to their team, can't be confused with other concepts, and makes sense within the context of the codebase they are working in. While it's definitely more of an art than an exact science, these challenges tend to make good variable naming a difficult task for developers.
In your view, what are the key characteristics that make a variable name clear, concise, and consistent? Could you provide an example of a well-named variable and explain why it's effective?
I'd answer, but I'd hate to spoil my talk 😉 Come listen to it at Visual Studio Live instead!
Can you share a before-and-after example where you improved a variable name and what your thought process and rationale were behind the change?
We actually go through a few examples in my talk where we improve it in real-time with the audience! In essence, we take a very vague, ambiguous and concept-void variable name and slowly iterate on it to become more concise, meaningful and context-filled.
What is one example guideline or best practice you would recommend for developers to follow when naming variables to ensure clarity and consistency?
When naming variables that are integers, be explicit! For example, say you're naming a variable that holds the amount of delay (in milliseconds) for a tooltip. Instead of tooltipDelay, a better name could be tooltipDelayInMilliseconds. When you're dealing with a number or count of something, say so! For example, if you have a variable that holds how many accounts are currently being requested, numberOfAccounts or numberOfRequestedAccounts is much more explicit than just accounts. Yes, the variable names are a bit longer. However, the cognitive load you remove for that extra effort to make them explicit can make a world of a difference when reading, re-reading and understanding code.
For developers who are just starting out, what strategies or exercises can they use to develop their skills in naming variables effectively? How can they get better at this seemingly simple yet complex task?
Go back to some code you've written in the past and see if there are variables that you can improve. Are there parts that you re-read or have trouble understanding? Would a more meaningful variable name help? If so, change those variables! Another thing you can do: Moving forward, resist the temptation to use "easy" variables. As you write code, take some time to think of a more meaningful variable name than temp, user, item, or other common concepts. Instead, consider the domain you are in, what the code is doing, and what concepts you are trying to convey. You can think of it as making your code a bit more wordy or verbose, but in reality, you're making it more readable and robust. And you're helping your future self when you have to re-read in a few months; you'll know exactly what you meant by being so explicit!
Note: Those wishing to attend the conference can save hundreds of dollars by registering early, according to the event's pricing page. "Register for VSLive! Chicago by the March 1 Super Early Bird deadline to save up to $400 and secure your seat for intensive developer training in Chicago!" said the organizer of the developer conference, which is presented by the parent company of Visual Studio Magazine.
Posted by David Ramel on 02/20/20240 comments

Creating AI-powered applications is a natural fit for the Microsoft Azure cloud, but sorting out all the different options for the backing data stores can seem daunting.
All developers are looking for an edge to build applications that are data-driven and harness the power AI, and Azure Databases provide a range of options for secure, scalable and highly available data applications using all the latest languages.
Microsoft's "Databases on Azure" guidance sums up many of the different options: "Develop AI-ready, trusted applications with a range of relational and non-relational databases and keep your focus on application development and innovation, not database management. Intelligence built-in helps automate management tasks like high availability, scaling, and query performance tuning so your applications are always on and ready. Trust Azure for built-in data security controls, broad regional coverage, and more compliance offerings to help strengthen your security posture and support your business growth."
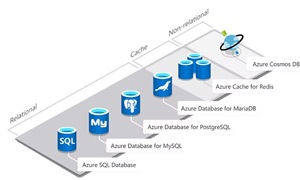 [Click on image for larger view.] Azure Databases (source: Microsoft).
[Click on image for larger view.] Azure Databases (source: Microsoft).
Some of the options Azure offers include :
Purpose-Built Cloud Databases
- Azure Cosmos DB: Fast, distributed NoSQL and relational database at any scale -- Develop high-performance applications of any size or scale with a fully managed and serverless distributed database supporting open source PostgreSQL, MongoDB, and Apache Cassandra as well as Java, Node.JS, Python, and .NET.
- Azure SQL Database: Flexible, fast, and elastic SQL database for your new apps -- Build apps that scale with a fully managed and intelligent SQL database built for the cloud. Grow your applications with near-limitless storage capacity and responsive serverless compute, backed by AI-based advanced security.
Open Source Databases
- Azure Database for PostgreSQL: Fully managed, intelligent, and scalable PostgreSQL database -- Innovate faster with a fully managed PostgreSQL database service for open-source developers building scalable and secure enterprise-ready apps.
- Azure Database for MySQL: Scalable, open-source MySQL database -- Develop apps with a fully managed community MySQL database service delivering high availability, mission-critical performance, and elastic scaling for open-source developers building mobile and web apps.
- Azure Database for MariaDB: Fully managed, community MariaDB -- Build with a fully managed community MariaDB database service delivering high availability and elastic scaling for open-source developers.
- Azure Cache for Redis: Distributed, in-memory, scalable caching -- Accelerate your application's data layer with an in-memory data store that offers increased speed and scale for web applications, backed by the open-source Redis server.
Sorting out all those options and choosing the right tech for your particular application is so important it's the topic of a keynote address at the upcoming Visual Studio Live! developer conference slated for March in Las Vegas.
The keynote, titled "Developing Modern Data Applications Using the Power of AI with Azure Databases," will show you when and where to use the family of Azure Databases including Azure SQL Database, Azure Database for PostgreSQL, Azure Cosmos DB, and Azure Database for MySQL.
"You will see how to build applications to power AI applications driven by data and also AI technologies that speed up your development and improve quality with Microsoft Copilot technologies," said Bob Ward, one of the keynote presenters. The Principal Architect for Microsoft Azure Data will be presenting along with Davide Mauri, Principal Product Manager at Microsoft.
"You will also see various new options on how to use new techniques to access data with less code and integrate your data with Microsoft Fabric," Ward said.
Attendees are promised to learn:
- When and where to use various Azure Database choices
- How to build-driven AI applications and how to use Copilot experiences to improve the developer experience
- New experiences on how to access your data to save time and code
We recently caught up with Ward to learn more about his March 6 keynote in a short Q&A.
VSLive! You have such an impressive background. What inspired you to first get involved in data-driven development?
Ward: My first data development projects were on Unix systems writing C code with Ingres (the predecessor of today's PostgreSQL). I was working on healthcare applications, and I saw from that moment how important data is to any business or application. And I found out it was helpful to not just learn to build great code but learn the database side as well to write efficient queries and understand how a database worked. Learning these skills together helped really give me so many career opportunities.
With various Azure Database options like Azure SQL Database, Azure Database for PostgreSQL, Cosmos DB and Azure Database for MySQL, how does a developer determine the best choice for a particular data-driven application?
I realize looking at this lineup can feel a bit overwhelming. We will talk more about this in the keynote, but here is a way to look at it. If you like SQL Server and this is your preferred choice, then Azure SQL Database is perfect for you. But I have some customers who prefer an open source database and still want that "relational" feel. So, I tell him if you want to go that route, we have excellent options for managed cloud databases such as Azure PostgreSQL or MySQL per your choice and experiences. Azure Cosmos DB has traditionally been thought of as a "NoSQL" database. If you love working with native JSON data, you can easily use Cosmos DB. Cosmos DB now also offers experiences including integration with PostgreSQL and MongoDB.
 "The great thing about all of these database options is that they take advantage of the power of Azure. This includes experiences for your favorite APIs and managed security, scalability, and availability. But most importantly all of them can be used to build new AI data-driven applications integrating with services like Azure OpenAI. We will talk about this in the keynote and have demos for you to see it in action."
"The great thing about all of these database options is that they take advantage of the power of Azure. This includes experiences for your favorite APIs and managed security, scalability, and availability. But most importantly all of them can be used to build new AI data-driven applications integrating with services like Azure OpenAI. We will talk about this in the keynote and have demos for you to see it in action."
Bob Ward, Principal Architect, Microsoft Azure Data, Microsoft
The great thing about all of these database options is that they take advantage of the power of Azure. This includes experiences for your favorite APIs and managed security, scalability, and availability. But most importantly all of them can be used to build new AI data-driven applications integrating with services like Azure OpenAI. We will talk about this in the keynote and have demos for you to see it in action.
In your personal experience, can you share one example of how GitHub Copilot and Chat improve the development process and enhance quality?
I can't wait to show some of the innovations here for developers. For me already the capabilities for GitHub Copilot to help me get started to build data applications is incredible, all right within the comfort of tools like Visual Studio or VS Code. But there are some other new experiences people may not know about -- our Microsoft Copilot story -- that will help developers. And we can't wait to show it to you during the keynote.
What future trends do you foresee in the integration of AI and database technologies?
Right now it feels the huge need is to build generative AI applications, but with their data. And there are many different methods to do this. So, what I see in the future is a merging of these methods into a smaller set of options that give developers the best way to build these applications quickly. I also see the concept of hybrid searching and even the use of small language models to become more popular over time. And per the previous question on Copilots, I believe we will see an explosion of this to help developers build and ship code faster but more efficient, performant, secure and with fewer bugs.
What do you hope people take away from your keynote?
The most important takeaway I want people to get from the keynote is that Azure Databases all-up are fully managed cloud database services you can rely on today and in the future to build intelligent AI data-driven applications. Our team is committed to staying on top of all the new innovations in AI and ensuring developers have what they need for real-world applications that are data driven using the power of AI without having to give up on the tried-and-true database capabilities of security, scalability and availability.
Note: Those wishing to attend the conference can save hundreds of dollars by registering early, according to the event's pricing page. "Register for VSLive! Las Vegas by the Feb. 9 Extended Early Bird Deadline to save $300 and secure your seat for intensive developer training in exciting Las Vegas!" said the organizer of the developer conference.
Posted by David Ramel on 02/05/20240 comments

Hey, everyone! I'm Mickey Gousset, a staff DevOps architect at GitHub, and I am thrilled to be contributing to the VSLive! blog as a monthly how-to columnist. While every month you can expect tips, tricks and best-practices advice from the development world, for this installment, I thought I'd share some of my predictions for 2024 in the field of software development.
Predicting the future of software development is always an intriguing task, as the field is rapidly evolving. Here are my top three predictions for the software development landscape in 2024.
1. The Rise of AI-Driven Development
OK, you knew this was going to be at the top of the list. ChatGPT took the world by storm in 2023. AI technologies, like machine learning and natural language processing, are becoming sophisticated enough to assist in code generation, bug fixes and even in making design decisions.
In 2024, tools like GitHub Copilot that suggest code snippets will become more advanced, helping reduce development time and improve code quality. AI will play a more integral role in software development, from initial design to testing and deployment. AI-driven development tools will continue to enhance developer productivity and creativity.
If you're curious about all this, look into attending VSLive! Las Vegas this year, where we have an entire track dedicated to "cutting-edge AI."
2. Growth in Cross-Platform Development
The demand for cross-platform development tools will continue to increase, as businesses seek to target multiple platforms (iOS, Android, Web, desktop) simultaneously.
As the mobile market continues to grow and the lines between desktop and mobile blur, developers are looking for efficient ways to build applications for multiple platforms. Cross-platform frameworks provide a cost-effective solution, enabling a single codebase to run on various platforms. We can expect significant improvements in these frameworks, with better performance, more native features and easier debugging.
For example, MAUI is a cross-platform framework introduced by Microsoft as part of .NET 6. It's an evolution of Xamarin.Forms, designed to created native mobile and desktop apps with a single codebase. You can learn more about MAUI on the "Developing New Experiences" track at VSLive! Las Vegas.
3. Continued Emphasis on DevOps and Automation
DevOps practices and automation will become more deeply ingrained in the software development process. Continuous integration and deployment (CI/CD) will continue to evolve, and automation will extend to more areas, such as security (DevSecOps).
The integration of development and operations has been proven to enhance efficiency, reduce errors and speed up deployment. In 2024, we can expect DevOps to evolve further, incorporating more automated processes all while not sacrificing quality. Tools that facilitate continuous testing, integration and monitoring will be crucial. The integration of security into the DevOps pipeline will also be a major focus.
If you're going to be at VSLive! Las Vegas, you can learn the latest on these evolutions in the "Modern Software Engineering" track.
Now, I don't have a crystal ball. I'm sure there is a trend I may have missed, or one that will jump to the top of the stack. But these three areas are definitely worth keeping an eye on. And keep an eye on this blog for future information, tips and tricks for the development world.
Posted by Mickey Gousset on 01/17/20240 comments